Home / CRM Software
- Overview
- High Rated
- Easiest to Use
- Free
- Resources
Find the right fit for you
Get an overview of the CRM
category at a glance
Market Segments
Star Rating
Languages Supported
Best CRM Software
CRM software is most commonly implemented in sales departments to act as the central hub for sales force automation, including contact, account, and opportunity management. CRM software is often delivered separately from other enterprise solutions, such as ERP systems, marketing automation software, and customer service software, but is often integrated with other business applications to facilitate an enhanced and coordinated customer experience.
Top 10 CRM Software
- Salesforce
- HubSpot Sales Hub
- ActiveCampaign
- Zoho
- Freshsales
- Pipedrive
- monday.com
- SharpSpring
- Keap (formerly Infusionsoft)
- Thryv
Compare CRM Software
- Optimized for quick response
Entry Level Price:$25 /user/month*
Salesforce helps businesses of all sizes accelerate sales, automate tasks and make smarter decisions so you can grow your business faster. Salesforce CRM offers: – Lead & Contact Management – Sales Opportunity Management – Workflow Rules & Automation – Customizable Reports & Dashboards – Mobile Application
- Optimized for quick response
Entry Level Price:$25 /user/month*
Salesforce helps businesses of all sizes accelerate sales, automate tasks and make smarter decisions so you can grow your business faster. Salesforce CRM offers: – Lead & Contact Management – Sales Opportunity Management – Workflow Rules & Automation – Customizable Reports & Dashboards – Mobile Application
- Optimized for quick response
Entry Level Price:$25 /user/month*
Salesforce helps businesses of all sizes accelerate sales, automate tasks and make smarter decisions so you can grow your business faster. Salesforce CRM offers: – Lead & Contact Management – Sales Opportunity Management – Workflow Rules & Automation – Customizable Reports & Dashboards – Mobile Application
- Optimized for quick response
Entry Level Price:$25 /user/month*
Salesforce helps businesses of all sizes accelerate sales, automate tasks and make smarter decisions so you can grow your business faster. Salesforce CRM offers: – Lead & Contact Management – Sales Opportunity Management – Workflow Rules & Automation – Customizable Reports & Dashboards – Mobile Application
- Optimized for quick response
Entry Level Price:$25 /user/month*
Salesforce helps businesses of all sizes accelerate sales, automate tasks and make smarter decisions so you can grow your business faster. Salesforce CRM offers: – Lead & Contact Management – Sales Opportunity Management – Workflow Rules & Automation – Customizable Reports & Dashboards – Mobile Application
- Optimized for quick response
Entry Level Price:$25 /user/month*
Salesforce helps businesses of all sizes accelerate sales, automate tasks and make smarter decisions so you can grow your business faster. Salesforce CRM offers: – Lead & Contact Management – Sales Opportunity Management – Workflow Rules & Automation – Customizable Reports & Dashboards – Mobile Application
- Optimized for quick response
Entry Level Price:$25 /user/month*
Salesforce helps businesses of all sizes accelerate sales, automate tasks and make smarter decisions so you can grow your business faster. Salesforce CRM offers: – Lead & Contact Management – Sales Opportunity Management – Workflow Rules & Automation – Customizable Reports & Dashboards – Mobile Application
- Optimized for quick response
Entry Level Price:$25 /user/month*
Salesforce helps businesses of all sizes accelerate sales, automate tasks and make smarter decisions so you can grow your business faster. Salesforce CRM offers: – Lead & Contact Management – Sales Opportunity Management – Workflow Rules & Automation – Customizable Reports & Dashboards – Mobile Application
- Optimized for quick response
Entry Level Price:$25 /user/month*
Salesforce helps businesses of all sizes accelerate sales, automate tasks and make smarter decisions so you can grow your business faster. Salesforce CRM offers: – Lead & Contact Management – Sales Opportunity Management – Workflow Rules & Automation – Customizable Reports & Dashboards – Mobile Application
- Optimized for quick response
Entry Level Price:$25 /user/month*
Salesforce helps businesses of all sizes accelerate sales, automate tasks and make smarter decisions so you can grow your business faster. Salesforce CRM offers: – Lead & Contact Management – Sales Opportunity Management – Workflow Rules & Automation – Customizable Reports & Dashboards – Mobile Application
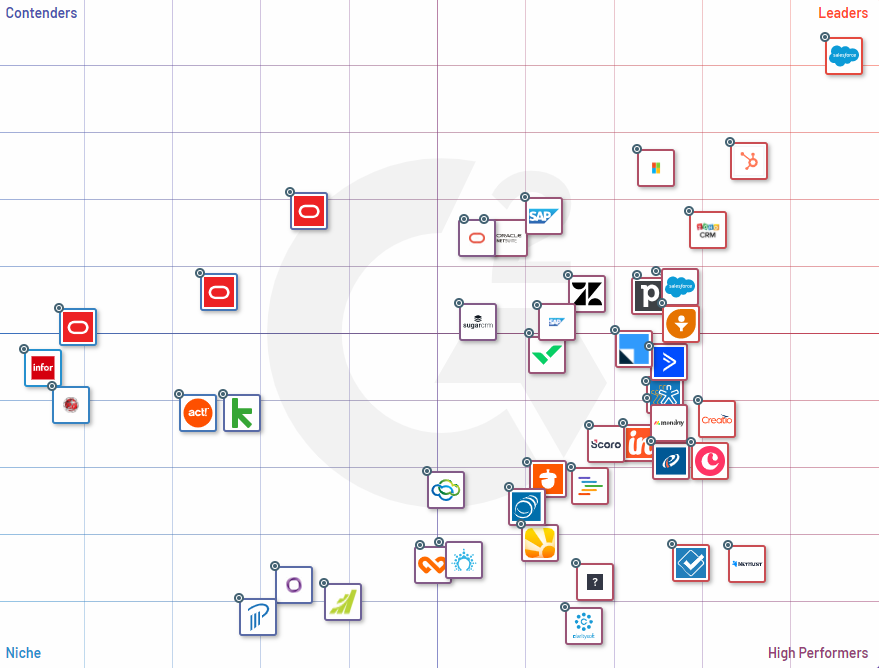
Select Grid® View
TDH Grid® for CRM
Check out the TDH Grid® for the top CRM Software products. G2 scores products and sellers based on reviews gathered from our user community, as well as data aggregated from online sources and social networks. Together, these scores are mapped on our proprietary G2 Grid®, which you can use to compare products, streamline the buying process, and quickly identify the best products based on the experiences of your peers.
CRM Topics
- What is CRM Software?
- What are the Common Features of CRM Software?
- What are the Benefits of CRM Software?
- Who Uses CRM Software?
- Challenges with CRM Software?
- Which Companies Should Buy CRM Software?
- How to Buy CRM Software?
- What Does CRM Software costs?
- Implementation of CRM Software costs?
- CRM Software trends
Learn More About CRM Software
What is CRM Software?
CRM software unites all customer and prospect data in a single tool, bringing added visibility into customer interactions. A CRM is the center of any successful sales organization, the database in which all data, interactions, and notes are stored. Organizations use CRM systems to ensure that contact and interaction data can be easily located, sorted and amended as necessary throughout the customer lifecycle. Contacts can be stored hierarchically under a single company or organization, giving sales teams a holistic view of interactions with all relevant employees of a prospect or customer.
What Does CRM Stand For?
CRM stands for customer relationship management, which refers to how a business manages its relationships with clients or prospects.
What Types of CRM Software Exist?
Industry-specific CRM software
CRMs can be catered to a variety of different industries. For example, there are CRMs catered for public relations or PR CRM software, financial services CRM software, mortgage CRM software, etc. In this sense, if a buyer is looking for a CRM that is catered to their particular industry, then it is possible to find a CRM that can address their individual needs.
All-in-one CRM solutions
The majority of CRM solutions fall into an industry-agnostic offering that is simply meant to help businesses manage their client relationships, client contact information, and client interactions, however, all-in-one CRM solutions emerged in the market due in part to an increase in demand for CRM applications among smaller businesses. These all-in-one solutions offer a series of integrated customer-related features attractive to small and mid-market companies.
CRM software provides exclusively sales-related features, such as contact, account, and pipeline management. These features are typically robust enough for use by large sales teams, with advanced reporting capabilities and user dashboards. These products are commonly marketed to and used by mid-market and enterprise sales organizations.
All-in-one CRM products offer a collection of integrated functions that vary in complexity but are designed to help small businesses manage customer interactions across their websites. These include traditional CRM features, such as lead management or simple email marketing, in addition to other features such as website management and digital commerce tools.
CRM software products are delivered as either a standalone platform or as a series of sales-centric modules. These modules encompass sales force automation functions and integrate with each other to form a unified solution. Other functions, such as marketing automation and customer support, are often implemented separately from the standalone CRM system.
All-in-one CRM products are packaged and sold as an integrated system with built-in tools designed to address a wide range of business issues. These products typically are implemented in place of traditional CRM products, and can also supplant the need for disparate systems such as ERP, HCM, and accounting software.
What are the Common Features of CRM Software?
The following are some core features within CRM software that can help users in a few ways:
Account and contact management: One of the core features of a CRM is extensive account and contact management. Contact management features allow users to sort contacts by the accounts they are associated with. This allows users to have key contact information such as phone numbers and email addresses of various roles at any given company. This way if someone wants to contact a product marketing manager or even the CRO at a company they can quickly reference the contacts associated with the account.
Opportunity management: Another core feature of CRM software is opportunity management. This allows users to track a sales opportunity through its various stages, forecast the likelihood of closing an opportunity, take notes on customer pain points and needs, and track opportunity quotes. As an opportunity moves through the various stages, users can assign a percentage chance to the deal closing as well as mark if an account renewal is at risk of being lost. This will highlight a call to action for salespeople and will alert them that they might need to address any customer concerns to increase the likelihood that they will sign a deal. Additionally, within the opportunity section, salespeople can assign quotes for the deal based on how the deal is progressing. This helps salespeople give an accurate quote to a potential customer and forecast revenue for the fiscal year.
Lastly, it’s crucial for users to take diligent notes on customer needs as the deal progresses. For example, if a call was conducted and the potential customer indicated their pain points and what’s most important to them, users can record that within the opportunity page on the CRM. This allows salespeople to come back with their needs addressed and increases the likelihood of closing a deal.
Lead management: Lead management features are another core feature of a CRM that can help drive more revenue for businesses. When a lead filters into the company, whether that be from an event, an online form, or tracking online visitors, the CRM can automatically store a lead’s contact information as well as provide additional features to help pursue the lead. For example, CRMs generally provide lead scoring features that automatically determine the best leads to chase based on various factors including how that lead has already interacted with the business website. If a lead has visited certain pages or downloaded certain resources, it may be a good indicator of what product or solution they are looking for.
Additionally, CRMs can filter in important demographics and make it easy to visualize lead information such as job titles, company size, company revenue, and more. This further makes it easier to filter out leads that businesses shouldn’t waste time pursuing.
What are the Benefits of CRM Software?
Keeping track of customer interactions: The core benefit of a CRM revolves around keeping track of customer interactions. This includes interactions such as phone calls, emails, or in-person meetings. Salespeople can track where customers and prospects are in the buying cycle to determine appropriate levels of contact and opportunities for upsells or engagement. This full picture view of the company’s interactions with a customer ensures that anyone throughout the company can know where a customer relationship stands at any given time.
Improved organization: CRMs provide users with a 360-degree view of customer interactions across all departments within the organization, increasing collaboration and ensuring a single, informed customer experience. Having all customer contact information and interactions in one space makes it easy to access all information about a customer, thus improving customer relationships.
Increased revenue: The ultimate goal of implementing a CRM is to increase sales revenue. By having more detailed information on customer pain points, businesses will have a better understanding of what needs must be addressed with potential customers. This allows businesses to close more deals and secure more revenue.
Who Uses CRM Software?
The majority of workers at a B2B company will frequently access a CRM. This is because it houses customer information such as email addresses, job titles, social media accounts, and other key revenue data. However, below are the teams that will likely use CRM software more often:
Sales and business development teams: A CRM is traditionally a sales tool, providing sales representatives and management teams with the information and insights they need throughout the sales process. A 360-degree view of the customer or prospect helps sales teams drive smarter selling decisions. These tools increase organization and streamline tracking client information, letting salespeople focus on selling.
Business development representatives can start their interactions with prospects and record all notes and conversations in the CRM. From there, it’s easy to hand the prospect over to a new sales account owner when they are ready to engage or buy. Sales representatives immediately gain access to the client’s history up to that point, catching them up to speed with minimal impact on employee time or resources.
Sales managers and leaders can also benefit from the reporting and recordkeeping functionality of a CRM, gaining visibility into which team members are hitting goals, at-risk accounts, and more.
Marketing teams: Successful sales and marketing teams work in alignment, and being immersed in the company’s CRM will help marketing better support their sales counterparts. Viewing every lead and opportunity helps to inform marketing campaigns, giving marketers a strong understanding of the sales pipeline and opportunity.
Within a CRM, contacts can be organized by their progress in the pipeline. This view of customers lets marketers segment targets for different communications. Additionally, as marketing works to qualify leads, they can pass those leads and their scores directly to the CRM tool.
Customer service teams:Customer service and success teams can track their interactions with customers and prospects in the CRM, creating a full picture of how the customer is interacting with all departments within the company, not just sales. This gives any employee visibility into issues or questions their customers may have and enables communication between teams to determine who should potentially follow up with the contact. Some CRM tools even integrate with help desk software, automatically pulling customer interactions into the CRM and avoiding the need for manual updates.
Software Related to CRM Software
There are many types of software that can be used in conjunction with a CRM. This can include ERP systems, marketing automation tools, business intelligence tools, or any software that houses company data. If the business already has valuable information stored in software, it can be useful to integrate or migrate that data over to a CRM. Aside from this, below is a list of tools that can be used in conjunction with CRMs to enhance the effectiveness of the CRM:
Sales analytics software: Sales analytics systems are usually implemented on top of sales force automation and other CRM systems and use existing data to reveal insights, though some serve as both the CRM system of record as well as the analytics tool.
Lead-to-account matching and routing software: Lead-to-account matching and routing software automatically matches new leads to the correct account record in a CRM and then routes those leads to the correct salesperson according to the organization’s territory mapping. While some CRMs have native capabilities to do this, most perform lead-to-account matching at a minimal capacity, which is why it can be very useful to implement a standalone lead-to-account matching and routing solution.
Proposal software: Proposal software is designed to streamline and automate the proposal and request for proposal (RFP) process for sales operations. Proposal software works nicely with CRMs as a way to easily pull product and customer data from the CRM and streamline the proposal process.
CPQ software: CPQ software is used in sales departments to accelerate the sales process while improving quote accuracy and customer relations. At some point in the sales cycle, the customer is going to ask for a rough estimate on how much some product is going to cost them. CPQ software can automate the process of generating a quote which makes it easier to give prospects quick answers, and as a result, accelerate the time it takes to close a deal. Having CPQ software integrated within a CRM can have all this information in one place, making it easier for salespeople to close deals.
Challenges with CRM software
Overwhelming amount of features: CRMs can be packed with useful features such as lead management automation, analytics, email management, and more. However, businesses often ignore these extra features and focus strictly on the opportunity management and contact management aspect of a CRM. While these should be the main focus of a CRM, the software does function as a one-stop solution for many other business processes such as marketing, customer service, sales forecasting, etc.
Odds are that a business is paying a hefty sum for all of these additional features as well, so it’s essential to take advantage of them. To become more informed on the many features a CRM may offer, it can be helpful to access online knowledge bases for the particular CRM of choice. This can include videos and tutorials on how to access helpful features.
Dated information: CRMs are meant to function as a repository of contact information. However, it can be challenging to keep this information constantly up to date especially when contacts change companies or emails. To combat this common issue and remove outdated or duplicate contacts, users should perform periodic cleanings of the CRM.
Change management: It is challenging for employees to change their work habits to adapt to a CRM. CRMs can be substantial in size and have countless features and peculiarities to figure out. Some employees may choose to keep doing things the old way with contact management, using excel sheets and notes. Hence, companies should have several resource managers who can help answer questions and guide new employees to having a successful relationship with a new CRM. This all starts with solid onboarding and consistent training.
Which Companies Should Buy CRM Software?
Every company that has a long list of customers and a need to better organize customer contact information can benefit from a CRM. Whether the industry is automotive or food and beverage, every business can utilize a CRM to manage the sales pipeline and log accounts of customer interactions. While most businesses in most industries can take advantage of a CRM, different business sizes may have different needs. Here are the main three business-size buckets and their CRM needs.
Small business CRM: Typically, smaller companies desire CRM software that is easy to learn and offers a wide variety of high-level features. Small businesses may also want to consider implementing a CRM all-in-one solution, rather than a standalone CRM. These tools are often geared toward smaller organizations that want to have more lightweight CRM and marketing automation functionality incorporated into a single tool.
Mid-market CRM:Mid-market businesses are often in transition when it comes to CRM—they have outgrown their starter solution, but aren’t ready to commit to an enterprise-level tool that may come with more features or higher cost than they deem necessary. Many mid-market growth businesses find themselves pushing a lightweight tool to its limits, and beyond, not wanting to commit to a heavier solution. But this hinders their potential to grow their CRM strategy. Scalability is one of the most important features of a CRM for mid-market businesses.
Enterprise CRM:There are plenty of CRM tools to suit enterprise businesses. Larger companies often have more customer-facing departments, leading them to seek out a tool that handles more complex use cases and can scale to thousands of users. A trade-off with some of these systems is that they can take longer to implement and require more training. These tools are often highly customizable, but those customizations take time and developer resources. Enterprise companies typically employ at least one CRM administrator to support questions and needs across teams.
How to Buy CRM Software
Requirements Gathering (RFI/RFP) for CRM Software
Requirements gathering for CRM software is critical to ensure that the business is implementing a product that meets all of their needs. To do so, businesses must evaluate the critical needs below:
Compare CRM Software Products
Create a long list
Long lists are created by eliminating software options that do not provide critical functionality. To make a long list for a CRM, a buyer should look at the following functionalities and deem which products provide the necessary functionality:
- Contact management
- Sales performance management
- Sales collaboration
- Sales forecasting
- Lead management
- Lead assignment rules or lead routing
- Custom pipelines
- Product level quotes
- Marketing lead management
- Marketing lead management
- Email list management
- Campaign management
- Social media management
- Event marketing and webinars
- Lead generation tracking
- Lead scoring
- Integration with marketing automation software
Create a short list
Once a buyer has narrowed down their list from the following functionality above, it’s then important to get even more specific requirements. For example, if a company is looking for features catered to specific industries such as manufacturing or nonprofit, then there might be an industry-specific CRM that’s out there for them. When looking for an industry-specific CRM, buyers can evaluate many of the specialty CRMs on G2 including PR CRM software, nonprofit CRM software, construction CRM software, financial services CRM software, mortgage CRM software, and real estate CRM software.
Conduct demos
Demos are one of the most important stages in the buying journey. This allows a buyer to sit through an actual product demo and see if the product matches all of the requirements. To make sure the demo runs smoothly, users must ensure that the vendor has all of the requirements beforehand so they can showcase their features properly. Some of the use cases that a business should ask the vendor to showcase are the following:
Workflow improvements: How does the CRM improve on the already existing contact management workflow. Will this CRM make processes faster and more efficient?
Adaptability: How difficult is it for users to adapt to this new software? Can they showcase how easy it would be for an unfamiliar user to get acquainted with the software?
Lead information gathering: How easy is it to quickly find information within the software. If a user is looking for a contact or a lead, how intuitive is the software so it will lead them to what they’re looking for quickly?
Selection of CRM Software
Choose a selection team
CRMs are the backbone of most sales and marketing processes within a business. So, choosing the right CRM software is a big decision and can be costly, so businesses need to ensure they have the right stakeholders involved that can help make the best decision. The selection team for CRM software should include at least the CRO, as well as managers from the enterprise sales team, customer success team, and marketing team. These are plausibly the teams that will use the CRM most often, and they should have the most input on desired features of the CRM software.
Negotiation
When negotiating during the purchasing stage, it is advisable to always start small in terms of licenses and functionality. As stated previously, a lot of users end up paying for additional licenses or features in a CRM that they don’t need. During this negotiation, vendors will try to convince buyers that they can offer discounts on more functionality or licenses if they buy in bulk, but most businesses don’t need this. If businesses end up needing a few more licenses down the road, they can always add as need be.
In addition to this, the selection team should always strive to have implementation and ongoing support fees included in the cost. This way if any ongoing support is needed then businesses can always contact their customer success or support representative.
Final decision
After the negotiation stage is conducted, the final decision requires buy-in from everyone on the selection team. It’s important to ensure that all requirements are met and the final decision is supported by everyone involved.
What Does CRM Software Cost?
There are a variety of factors that will play into both the upfront and ongoing cost of a CRM. For upfront costs, a business will pay for setup, any custom integrations, and training. The ongoing cost is the subscription cost to actually use the CRM. CRMs are usually run on a subscription model which means users will pay a monthly or yearly rate to use the CRM. The subscription model for CRMs are generally set up as either a per-user or a per-contact model.
Per-user model: The average price per user on a subscription CRM generally ranges anywhere from $30 to $80. While there are more premium or bare-bones CRMs that are either cheaper or more expensive than this, this will generally be the average price.
Per-contact model: Some CRMs charge on a per contact structure. These are often CRM all in ones that also include marketing tools. These are not on a per-user basis and instead, businesses are paying on the number of contacts they want to have in the CRM. This may be more cost effective depending on the number of people in the company.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Below is the breakdown of the estimated time to ROI according to the review data on G2 as of January 26, 2021:
- 50% of buyers see an ROI in 6 months or less
- 24.5% of buyers see an ROI in 7-12 months
- 11% of buyers see an ROI in 13-24 months
- 5% of buyers see an ROI from 24-36 months
- 7.5 %of buyers haven’t realized a full payback yet
Implementation of CRM Software
How is CRM Software Implemented?
According to G2 review data as of January 26, 2021, 66% of users were able to implement and go live with CRM software in under a month. While this data is promising, implementing CRM software can be a challenging process since it is such a major investment and highly utilized tool within a company. For this reason, businesses should establish a team of stakeholders that will be responsible for implementing the software and can go through the process.
Generally, this process is broken down into a few key stages: software installation, process review and needs analysis, design, configuration, and integrations, training, and post-implementation support.
Who is Responsible for CRM Software Implementation?
Since CRM is such an integral part of every business’s sales strategy, it’s important to have a handful of experts who can help with implementation. These experts should include a project manager, an application analyst, an applications developer, a QA test engineer, and at least two members from the sales leadership team.
The project manager will help establish deadlines so implementation times are met in a timely manner. An application analyst can help with migrating data from any previous software over to the CRM, and an application developer can help with any customization for the CRM. The QA testing engineer can help head any testing efforts and offer timely, relevant, and meaningful feedback. Lastly, leadership from sales teams can speak to any features that they feel are important or missing from the solution that might help the sales teams that they manage.
What Does the Implementation Process Look Like for CRM Software?
The implementation process starts by writing out a detailed plan on when certain steps in the implementation process will be completed. This is generally completed by the project manager and broken down into key four stages. These four stages include user training and engagement, data migration, testing, and then finally go live. Before launching the implementation process, relevant staff must be notified that the business is launching a new CRM to give them an opportunity to ask any questions on how this will impact their day-to-day operations.
When Should You Implement CRM Software?
A CRM should only be implemented when it has gone through the above-mentioned steps. With this in mind, businesses should expect this process to take at least a couple of months before they finally go live with the CRM. Even following the implementation, there should be resources readily available so users can receive additional training or mitigate any challenges they are having with using the CRM.
CRM Software Trends
Lead-to-account matching and routing
Lead-to-account matching and routing enables businesses to get a more comprehensive picture of leads and engagement within their account-based strategy, as well as follow up with captured leads at a quicker rate. This is a growing need in sales organizations as many businesses find it difficult to quickly route leads and oftentimes even find duplicate leads that are outdated within their CRM. Lead-to account matching has strong features that can identify duplicate leads and ensure that they aren’t imported into the CRM when there is already a pre-existing contact for the same person.
Artificial intelligence and CRMs
Automation in manual tasks can save workers tons of time in manual labor. In fact, there is even a separate type of software for automating manual sales tasks called AI sales assistant software. AI sales assistants often work alongside other programs or integrate with an existing CRM software, or sometimes even built within a CRM. AI sales assistants can automate manual tasks such as lead qualification and follow-up, pipeline management, forecasting, meeting scheduling, and data entry.
The Top 20 CRM Software
Check out this list of the top CRM Software products based on user satisfaction. A product’s satisfaction score is calculated by a proprietary algorithm that factors in real-user satisfaction ratings from review data. Software buyers can compare products according to their satisfaction scores to streamline the buying process and quickly identify the best products based on the experiences of their peers.
Top 10 CRM Software
- Salesforce
- HubSpot Sales Hub
- ActiveCampaign
- Zoho
- Freshsales
- Pipedrive
- monday.com
- SharpSpring
- Keap (formerly Infusionsoft)
- Thryv
#1

ActiveCampaign
Satisfaction
Setup and Support
Top Industries Represented
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
#2

ActiveCampaign
Satisfaction
Setup and Support
Top Industries Represented
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
#3

ActiveCampaign
Satisfaction
Setup and Support
Top Industries Represented
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
#4

ActiveCampaign
Satisfaction
Setup and Support
Top Industries Represented
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
#5

ActiveCampaign
Satisfaction
Setup and Support
Top Industries Represented
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
#6

ActiveCampaign
Satisfaction
Setup and Support
Top Industries Represented
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
#7

ActiveCampaign
Satisfaction
Setup and Support
Top Industries Represented
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
The Top 20 Easiest To Use CRM Software
See the top CRM Software products based on usability ratings. A product’s usability score is calculated by a proprietary algorithm that factors in real-user satisfaction ratings of how easy the product is to administer, as well as how well the product meets business requirements, among other ratings. Compare products according to their usability scores to streamline the buying process and quickly identify the best products based on real user experiences.
#1

ActiveCampaign
Setup and Support
Setup and Support
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
#2

ActiveCampaign
Setup and Support
Setup and Support
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
#3

ActiveCampaign
Setup and Support
Setup and Support
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
#4

ActiveCampaign
Setup and Support
Setup and Support
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
#5

ActiveCampaign
Setup and Support
Setup and Support
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
#6

ActiveCampaign
Setup and Support
Setup and Support
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
#7

ActiveCampaign
Setup and Support
Setup and Support
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
#9

ActiveCampaign
Setup and Support
Setup and Support
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
#10

ActiveCampaign
Setup and Support
Setup and Support
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
- Marketing and Advertising
Free
CRM software is most commonly implemented in sales departments to act as the central hub for sales force automation, including contact, account, and opportunity management. CRM software is often delivered separately from other enterprise solutions, such as ERP systems, marketing automation software, and customer service software, but is often integrated with other business applications to facilitate an enhanced and coordinated customer experience.
Top 10 CRM Software
- Salesforce
- HubSpot Sales Hub
- ActiveCampaign
- Zoho
- Freshsales
- Pipedrive
- monday.com
- SharpSpring
- Keap (formerly Infusionsoft)
- Thryv
- Optimized for quick response
Salesforce helps businesses of all sizes accelerate sales, automate tasks and make smarter decisions so you can grow your business faster. Salesforce CRM offers: – Lead & Contact Management – Sales Opportunity Management – Workflow Rules & Automation – Customizable Reports & Dashboards – Mobile Application
- Optimized for quick response
Salesforce helps businesses of all sizes accelerate sales, automate tasks and make smarter decisions so you can grow your business faster. Salesforce CRM offers: – Lead & Contact Management – Sales Opportunity Management – Workflow Rules & Automation – Customizable Reports & Dashboards – Mobile Application
- Optimized for quick response
Salesforce helps businesses of all sizes accelerate sales, automate tasks and make smarter decisions so you can grow your business faster. Salesforce CRM offers: – Lead & Contact Management – Sales Opportunity Management – Workflow Rules & Automation – Customizable Reports & Dashboards – Mobile Application
- Optimized for quick response
Salesforce helps businesses of all sizes accelerate sales, automate tasks and make smarter decisions so you can grow your business faster. Salesforce CRM offers: – Lead & Contact Management – Sales Opportunity Management – Workflow Rules & Automation – Customizable Reports & Dashboards – Mobile Application
- Optimized for quick response
Salesforce helps businesses of all sizes accelerate sales, automate tasks and make smarter decisions so you can grow your business faster. Salesforce CRM offers: – Lead & Contact Management – Sales Opportunity Management – Workflow Rules & Automation – Customizable Reports & Dashboards – Mobile Application
- Optimized for quick response
Salesforce helps businesses of all sizes accelerate sales, automate tasks and make smarter decisions so you can grow your business faster. Salesforce CRM offers: – Lead & Contact Management – Sales Opportunity Management – Workflow Rules & Automation – Customizable Reports & Dashboards – Mobile Application
- Optimized for quick response
Salesforce helps businesses of all sizes accelerate sales, automate tasks and make smarter decisions so you can grow your business faster. Salesforce CRM offers: – Lead & Contact Management – Sales Opportunity Management – Workflow Rules & Automation – Customizable Reports & Dashboards – Mobile Application
- Optimized for quick response
Salesforce helps businesses of all sizes accelerate sales, automate tasks and make smarter decisions so you can grow your business faster. Salesforce CRM offers: – Lead & Contact Management – Sales Opportunity Management – Workflow Rules & Automation – Customizable Reports & Dashboards – Mobile Application
- Optimized for quick response
Salesforce helps businesses of all sizes accelerate sales, automate tasks and make smarter decisions so you can grow your business faster. Salesforce CRM offers: – Lead & Contact Management – Sales Opportunity Management – Workflow Rules & Automation – Customizable Reports & Dashboards – Mobile Application
- Optimized for quick response
Salesforce helps businesses of all sizes accelerate sales, automate tasks and make smarter decisions so you can grow your business faster. Salesforce CRM offers: – Lead & Contact Management – Sales Opportunity Management – Workflow Rules & Automation – Customizable Reports & Dashboards – Mobile Application
Contents
- Glossary Terms
- Discussions
- Reports
CRM Software Resources
Articles, Glossary Terms, Discussions, and Reports to expand your knowledge on CRM Software
Resource pages are designed to give you a cross-section of information we have on specific categories. You’ll find articles from our experts, feature definitions, discussions from users like you, and reports from industry data.
CRM Software Articles

Increased Adoption of Lead-to-Account Matching and Routing Leads to New G2 Category
It’s no secret that it can be quite difficult to manage all inbound leads into an organization. When a lead form from a survey or marketing event is completed, the lead…

by Michael Gigante

Increased Adoption of Lead-to-Account Matching and Routing Leads to New G2 Category
It’s no secret that it can be quite difficult to manage all inbound leads into an organization. When a lead form from a survey or marketing event is completed, the lead…

by Michael Gigante

Increased Adoption of Lead-to-Account Matching and Routing Leads to New G2 Category
It’s no secret that it can be quite difficult to manage all inbound leads into an organization. When a lead form from a survey or marketing event is completed, the lead…

by Michael Gigante

Increased Adoption of Lead-to-Account Matching and Routing Leads to New G2 Category
It’s no secret that it can be quite difficult to manage all inbound leads into an organization. When a lead form from a survey or marketing event is completed, the lead…









